Vv(mr)
Vv(mr), the Void Volume, is the volume of space bounded by the surface texture from a plane at a height corresponding to a chosen “mr” value to the lowest valley. “mr” may be set to any value from 0% to 100%.
Vvv(p), the Dale Void Volume, is the volume of space bounded by the surface texture from a plane at a height corresponding to a material ratio (mr) level, “p” to the lowest valley. The default value for “p” is 80% but may be changed as needed.
Vvc(p,q), The Core Void Volume, is the volume of space bounded by the texture at heights corresponding to the material ratio values of “p” and “q”. The default value for “p” is 10% and the default value for “q” is 80%.
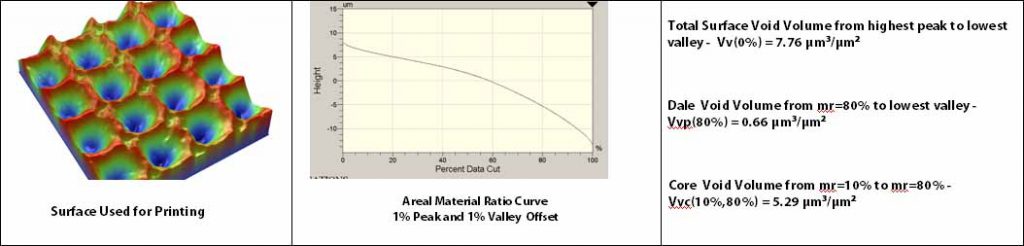
Example of Void, Dale Void and Core Void volumes. Note: The units for the Vv(mr), Vv(p) and Vvc(p,q) are um3/um2 – the void volume normalized by the cross sectional area of the measurement area. The peak offsets and valley offsets are applied prior to analysis.
Application
Vv(mr), Vvv(p) and Vvc(p,q) all indicate a measure of the void volume provided by the surface between various heights as established by the chosen material ratio(s) values. Thus these three void volume parameters indicate how much fluid would fill the surface (normalized to the measurement area) between the chosen material ratio values. For example, a Vv(25%) = 0.5 µm3/µm2 in (note how the units µm3/µm2 reduce to µm) that a 0.5 µm thick film over the measurement area would provide the same volume of fluid as needed to fill the measured surface from a height corresponding to mr=25% to the lowest valley.
The void volume parameters are useful when considering fluid flow, coating applications and debris entrapment. A new surface may be specified by Vv(0%) which would indicate the total initial void volume provided by the texture. The Core Void Volume , Vvc, may be useful to establish how much core space is available once a surface has been run-in resulting in decreased peak heights . The Dale Void Volume, Vvv(p) may be useful in indicating the potential remaining volume after significant wear of a surface has resulted.
